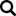Smart Nutrition for a Healthy Transition™
Hypocalcemia, low blood calcium, is the most prevalent metabolic disease of the transition dairy cow, affecting greater than 50 percent of all fresh dairy cows. Addressing this disease through proper nutrition and management may result in cows that are healthier, more productive and more profitable. Animate® is a new generation anionic mineral that helps to optimize calcium metabolism in the pre- and post-partum transition cow and may help reduce the incidence and negative impact hypocalcemia has on health, milk production and fertility.
Animate Delivers
Animate nutritional specialty product delivers the proper minerals needed by the cow to help optimize calcium metabolism. When fed at rates to maintain urine pH from 5.5 to 6.0, beginning at least 21 days prior to calving, Animate helps to optimize calcium metabolism through proper prepartum compensated metabolic acidosis which may result in healthier, more productive dairy cows. Designed based on science, formulated based on research, manufactured to the highest standards, and proven through years of research and field experience, Animate is the superior choice for proper negative DCAD balancing.


A culture and a philosophy that enables us to exceed expectations. Our integrated platform of innovative technology, based on sound science, knowledgeable teams and proactive programs, provides an advanced approach to unsurpassed quality. Through development, continual evaluation and improvement, our program stays a step ahead of industry standards to provide a quality product you can count on.
Don't Just Do DCAD, Do DCAD Right!
The program is simple. Fully acidify the cows, track them once a week and the transition period will go smooth.
I always say that the cows won’t lie to you. So you see it cow performance. And again, healthier cows and higher performance.
I think there’s a lot of companies that profess to do DCAD in some form or fashion, but what we’ve learned at Phibro over the last eight to ten years is that we do do it right, because of the performance that we can measure within the cows, metabolic events, fresh cow events, peak milk.
Animate Nutritional Specialty Product:
• PALATABLE: readily consumed without significantly depressing prepartum dry matter intakes, leading to higher postpartum dry matter intakes and, ultimately, increased milk yield.
• CONCENTRATED: one of the most concentrated commercially manufactured anionic products on the market. When fed in a fully acidogenic prepartum diet (urine pH from 5.5 to 6.0), Animate feeding rates are typically half the rate of other anionic products. This allows for more ration space and easier diet formulation.
• COMPLETE: uniquely formulated to provide effective levels of chloride and sulfur, plus other key nutrients such as magnesium and phosphorus, which are necessary for a proper negative DCAD diet formulation.

Expert Columns
Learn more about hypocalcemia and prepartum negative DCAD diets from industry experts.


Practical Application
Find practical information about feeding and managing a proper prepartum DCAD diet.
Download the app today to better track your dairy’s transition cow program!
By using the Animate App you are taking the next step to help monitor the performance of your prepartum DCAD diet. The Animate App is designed to help you track the factors
that impact transition cow performance, including ration DCAD, urine pH, bunk space,
stocking density, days in close up and other key parameters.
DAIRY FARMS
Set up and organize your dairy information
ENTER DATA
Enter data based on individual cow’s and farm details
VIEW DATA
View all data entered collectively by date.
HISTORICAL GRAPH
View & track trends of your herd over time.
Click below to for the web application or to download the App today on your iOS or Android system

Don’t Just Take Our Word for It.
Thousands of producers have put their trust in Animate nutritional specialty product for the livelihood of their cows.
Research and field studies conducted over many years, shows Animate is effective in supporting transition cows. Dairy owners in North America and elsewhere certainly agree. We’re proud to share these examples of producers who have experienced the difference Animate makes.

Mike Meyer
Meyer Family Dairy, Loyal, WI
“During low milk prices, we do everything possible. Our target at that point in life is that our cows and our people do not know that the milk prices are low. We’ve used OmniGen approximately 10 or 12… years. The OmniGen seems to increase the health of the cow — and a healthy cow is still our best bet in low milk prices.”

Mike Meyer
Meyer Family Dairy, Loyal, WI
“During low milk prices, we do everything possible. Our target at that point in life is that our cows and our people do not know that the milk prices are low. We’ve used OmniGen approximately 10 or 12… years. The OmniGen seems to increase the health of the cow — and a healthy cow is still our best bet in low milk prices.”

Mike Meyer
Meyer Family Dairy, Loyal, WI
“During low milk prices, we do everything possible. Our target at that point in life is that our cows and our people do not know that the milk prices are low. We’ve used OmniGen approximately 10 or 12… years. The OmniGen seems to increase the health of the cow — and a healthy cow is still our best bet in low milk prices.”
Frequently Asked Questions


Product information on this site may not be applicable in all countries. For completed product information and approved uses please contact your local Phibro representative.